Source: State Policy Dashboard
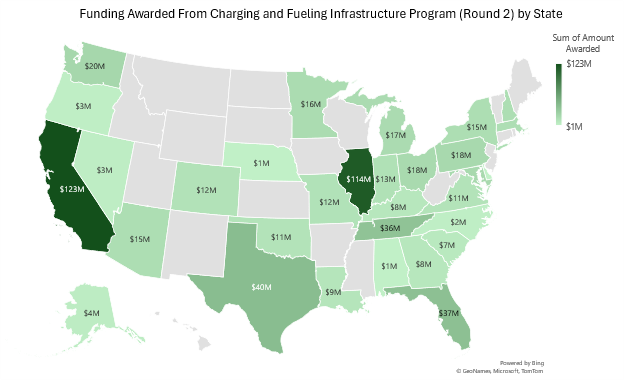
Last Friday, the Biden-Harris Administration announced $635 million in Round 2 funding through the Charging and Fueling Infrastructure (CFI) grant program. This funding aims to expand electric vehicle (EV) charging and alternative fueling infrastructure in communities and along highway corridors nationwide. With this latest round, the program has now awarded approximately 72 percent, or $1.8 billion, of its total funding, highlighting significant progress towards the implementation of this program.
To recap, this investment is part of a broader $2.5 billion commitment under the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act to build out EV charging infrastructure across two critical tracks: community charging and corridor charging. Community charging grants prioritize underserved, rural, and low-income areas, ensuring equitable access to EV infrastructure for all communities. In contrast, corridor charging grants focus on developing fueling infrastructure along designated Alternative Fuel Corridors (AFCs), which are essential for supporting long-distance travel. We have written about Round 1A and Round 1B funding awards in earlier digests.
The latest round of funding will support 49 projects across 27 states, four Federally Recognized Tribes, and the District of Columbia. These projects will deploy more than 11,500 EV charging ports, as well as hydrogen and natural gas fueling infrastructure. Of the $635 million awarded, $368 million will fund 42 projects aimed at expanding EV infrastructure in communities, including the installation of Level 2 and DC fast chargers. The remaining $268 million will support seven projects specifically installing EV charging and fueling infrastructure along AFCs. While nearly all funded projects focus on EV charging, some include funding for hydrogen and natural gas fueling infrastructure. Notably, nearly 67 percent of this round’s funding will be directed toward sites in disadvantaged communities, aligning with the federal Justice40 initiative.
Some of the awarded projects include:
-
Equitable Future-Ready Electrification Infrastructure for Green Heavy-duty Transportation (E-FREIGHT) in Illinois (Corridor): The Illinois Environmental Protection Agency received the largest funding award in this round ($100 million) to install 14 public EV charging stations along key freight corridors in the Chicago metro area. These stations will provide 345 charging ports and parking spaces, featuring battery storage and clean on-site power generation. Most of the stations will be located in areas that support nearby disadvantaged communities.
-
California-Nevada Zero-Emission Medium- and Heavy-Duty Drayage Infrastructure Project (Corridor): The California Energy Commission was awarded $55.9 million to install 21 public EV charging stations and one hydrogen refueling station for zero-emission medium- and heavy-duty trucks. The project will add at least 130 high-powered EV charging ports along busy routes in California and between Nevada, supporting clean freight transportation.
-
District of Columbia Round 2 Charging and Fueling Infrastructure Project (Community): The District of Columbia Department of Energy and Environment won $15 million to install 454 public EV charging ports at 220 locations, including retail centers, multifamily housing, car-sharing spots, curbside spaces, and public parking lots.
-
Twin Cities Charging and Fueling Infrastructure Discretionary Grant Program Competitive Solicitation (Community): Minnesota’s Metropolitan Council was awarded $15 million to install 1,875 EV charging ports across the region. The project will focus on serving renters, rural areas, low- and moderate-income neighborhoods, and environmental justice communities.
At least one more funding cycle is planned for the CFI program, with an expected allocation of at least $700 million. For more information on this round’s funding awards, visit our State Policy Dashboard.